Understanding Merged Mining: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction to Merged Mining
Merged mining, or Auxiliary Proof-of-Work (AuxPoW), is a powerful technique that allows miners to efficiently mine multiple cryptocurrencies simultaneously without sacrificing performance. Merged mining plays a crucial role in enhancing scalability and security within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. By leveraging the computational power of larger networks, smaller or newer blockchains can bolster their network stability and mitigate security risks.
How Merged Mining Works
At the centre of merged mining lies the Auxiliary Proof-of-Work (AuxPoW) system. This process enables miners to validate transactions and generate new blocks across multiple blockchains using a single proof-of-work algorithm.
Essentially, when miners operate on a parent blockchain, they can concurrently secure child blockchains without the need for additional hardware or energy. The relationship between parent and child chains is pivotal; the child chain benefits from the parent chain's robust hashing power.
Benefits of Merged Mining
Merged mining offers several advantages that enhance the security and efficiency of cryptocurrencies:
- Enhanced Security: Smaller blockchain networks gain robust security from larger networks like Bitcoin or Litecoin, making them more resistant to attacks.
- Increased Hash Rate: By pooling resources across multiple chains, merged mining elevates overall hash rates, contributing to improved network stability.
- Cost-Efficiency: Miners can reap rewards from different blockchains without incurring additional costs from separate mining setups.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Using existing computing resources for multiple networks significantly lowers energy consumption compared to traditional single-chain mining.
- Incentivization: Miners are motivated to secure various networks due to the potential for increased earnings from multiple sources.
Challenges and Limitations of Merged Mining
Despite its benefits, merged mining presents certain challenges:
- Potential Centralization: Larger miners might dominate the process, leading to centralization in smaller networks.
- Dependency on Parent Chain Security: Child chains heavily rely on their parent chains' security; any issues with a parent chain can adversely affect all connected child chains.
- Conflicts of Interest: Disagreements between parent and child chains might arise regarding governance or resource allocation.
Notable Merged Mining Examples
Several prominent cryptocurrencies have successfully implemented merged mining:
- Bitcoin and Namecoin: As one of the pioneering merged mining implementations, Namecoin enabled users to securely register domain names while benefiting from Bitcoin's hashing power since 2011.
- Litecoin and Dogecoin: In 2014, Dogecoin adopted merged mining with Litecoin to enhance network security following low miner participation due to reduced rewards.
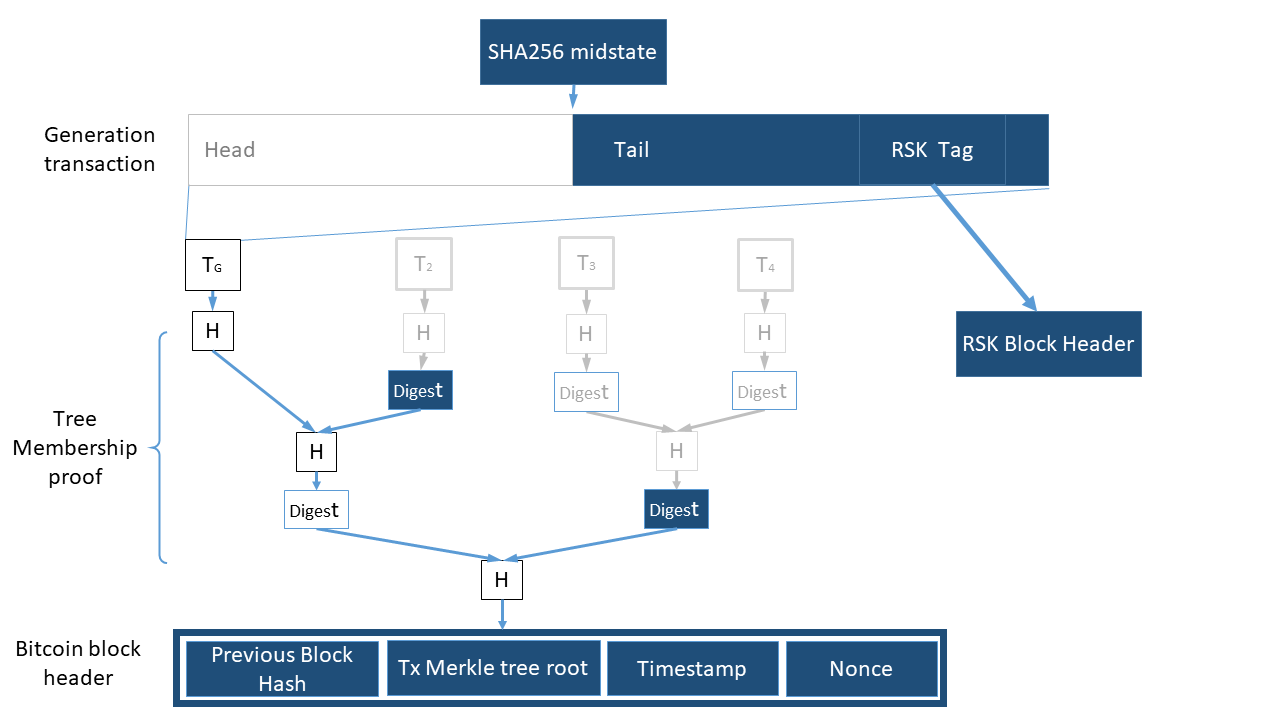
- Rootstock (RSK) with Bitcoin: RSK utilizes Bitcoin's network for its smart contracts platform through merged mining.
The Future of Merged Mining
Advancements are anticipated in the realm of merged mining:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations may yield more efficient algorithms that optimize resources across interconnected blockchains.
- Integration with Other Consensus Mechanisms: Future developments could see merged-mined blockchains seamlessly integrating with other consensus protocols, broadening their use cases in crypto ecosystems.
- Scalability Solutions: As scalability remains a challenge for many blockchain projects, merged mining could play an important role in addressing these issues while maintaining robust security standards.
Building on Rootstock
Rootstock, a sidechain of Bitcoin, utilizes merged mining to ensure that the same miners securing the Bitcoin network also secure the RSK network, without additional power consumption. Rootstock's full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) complements this strong security by enabling developers to port their existing Ethereum dApps to Rootstock with little modification.
Thirdweb offers a suite of tools, including client-side SDKs for user connections, scalable contract APIs backed by secure wallets, and pre-built, extendable contracts. This makes it easier than ever to create sophisticated web3 applications that benefit from Bitcoin's unparalleled security and Rootstock's enhanced transaction speeds and scalability.

