Understanding DeFi: A Comprehensive Guide to Decentralized Finance

Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has emerged as one of the most transformative and rapidly growing sectors in the blockchain space. By leveraging smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi aims to recreate traditional financial systems in a more open, transparent, and accessible manner. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore what DeFi is, how it works, its key components, and why it matters for developers and users alike.
What is DeFi?
DeFi refers to a ecosystem of financial applications built on blockchain networks, primarily Ethereum. Unlike traditional finance which relies on centralized intermediaries like banks, DeFi uses smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer financial services without middlemen. This includes lending, borrowing, trading, investing, and more - all powered by open-source protocols.
Some key characteristics of DeFi include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the system
- Transparency: All transactions and code are publicly visible
- Interoperability: Different protocols can easily integrate with each other
- Programmability: Automated smart contracts enable complex financial logic
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can participate
How DeFi Works
At its core, DeFi applications are powered by smart contracts deployed on blockchain networks. These self-executing contracts contain the rules and logic for how the protocol operates. Users can then interact with these contracts through dApps to access various financial services.
Here's a simplified flow of how a typical DeFi application works:
- User connects their wallet to a DeFi dApp
- User initiates a transaction (e.g. depositing funds into a lending pool)
- Transaction is sent to the blockchain
- Smart contract executes the logic (e.g. adding liquidity, calculating interest)
- State is updated on the blockchain
- User receives tokens representing their position (e.g. aTokens for Aave deposits)
This permissionless and automated approach allows DeFi to operate 24/7 without human intermediaries.
Key Components of DeFi
The DeFi ecosystem comprises several core building blocks that enable various financial use cases:
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
DEXs like Uniswap and SushiSwap allow users to swap tokens directly from their wallets without a centralized exchange. They use automated market maker (AMM) models to provide liquidity and determine prices.
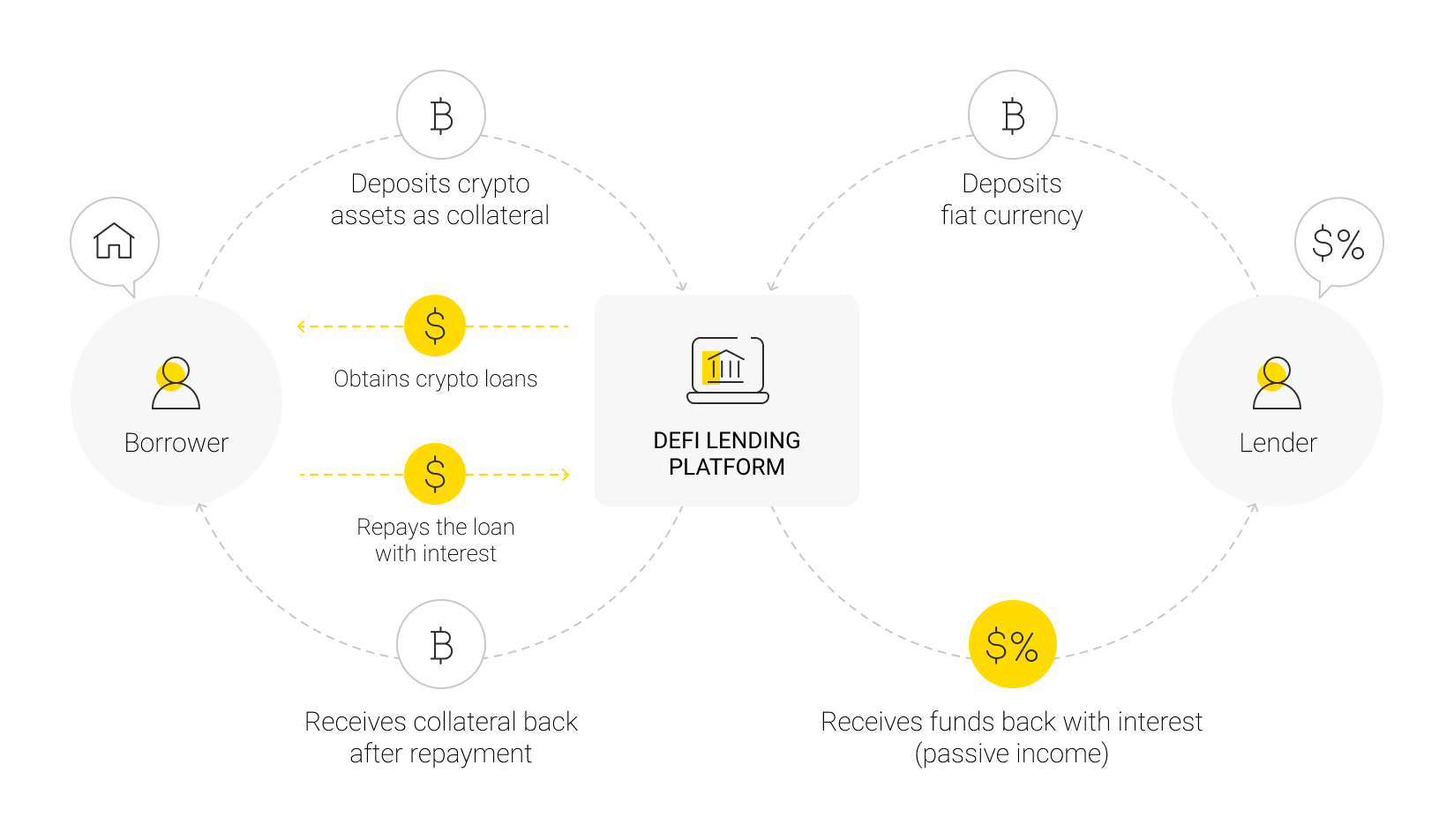
Lending Protocols
Platforms like Aave and Compound enable users to lend out their crypto assets to earn interest or borrow assets by posting collateral. Interest rates are determined algorithmically based on supply and demand.
Stablecoins
Cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies (like USDC or DAI) provide stability in the volatile crypto markets. They serve as an important bridge between DeFi and traditional finance.
Yield Farming
Users can earn additional tokens by providing liquidity to various DeFi protocols. This incentivizes participation and bootstraps liquidity for new projects.
Synthetic Assets
Protocols like Synthetix allow the creation of on-chain synthetic versions of real-world assets like stocks or commodities.
Insurance
Decentralized insurance protocols protect users against smart contract failures, hacks, and other DeFi-specific risks.
Benefits of DeFi
DeFi offers several advantages over traditional financial systems:
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can access DeFi services
- Transparency: All transactions are publicly visible on the blockchain
- Interoperability: Different protocols can easily integrate with each other
- Efficiency: Automated smart contracts reduce costs and enable 24/7 operation
- Innovation: Open-source nature allows rapid development of new financial products
Risks and Challenges
While promising, DeFi also comes with its own set of risks:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs in smart contract code can lead to hacks and loss of funds
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for DeFi remains unclear in many jurisdictions
- Scalability Issues: High gas fees on Ethereum can make smaller transactions uneconomical
- Complexity: DeFi can be difficult for newcomers to navigate safely
Building on DeFi with thirdweb
As a developer, you can leverage thirdweb's tools and SDKs to easily build and deploy DeFi applications. Our pre-built smart contracts and intuitive APIs simplify the process of creating token-based economies, NFT marketplaces, and other DeFi primitives.
Some ways you can use thirdweb for DeFi development:
- Deploy ERC20 tokens for your project
- Create NFT collections with royalties
- Build custom marketplaces for token swaps
- Implement on-chain governance for DAOs
- Integrate wallet connectivity and transactions
Check out our templates to get started quickly building with thirdweb.
The Future of DeFi
As the DeFi ecosystem continues to evolve, we're seeing exciting developments in areas like:
- Layer 2 scaling solutions to reduce gas fees
- Cross-chain interoperability protocols
- Real-world asset tokenization
- Decentralized identity and reputation systems
- Integration with traditional finance (TradFi)
The composability of DeFi protocols enables rapid innovation, with new projects building on top of existing primitives to create increasingly sophisticated financial products.

